The big bang is not a Reason to Believe!
A response to "A Response to Four Young-Earth Objections to Inflation"1
Astrophysicist Dr Jeff Zweerink works for the Hugh-Ross-led organization Reasons to Believe. He recently wrote the above article. Relevant portions of his words are reproduced (in green) with my comments interspersed.
A remarkable correspondence exists between inflationary big bang cosmology and the Bible’s accounts of the universe’s origin.
This is his summary statement, which one would assume that his article itself will support. But if you look deeply into the details the substance evaporates.
How can a correspondence exist between the biblical creation account and the big bang cosmogony (the study of the origin of the universe)? Leaving aside the elephant in the kitchen, the 6 ordinary days of Creation Week,2 just look at the respective sequences of events.
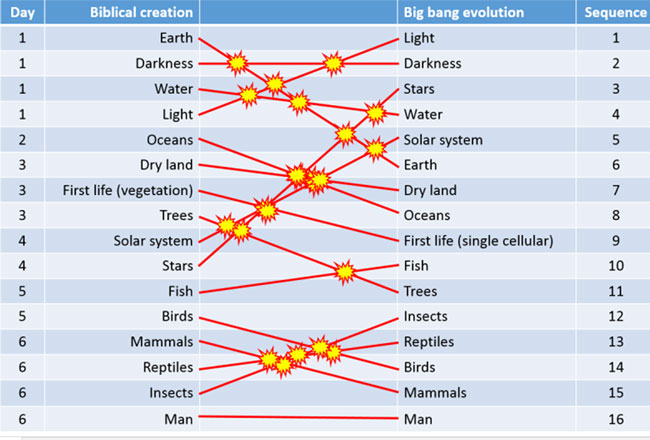
Credit: Idea from Russ Humphreys.
In the comparison to the Genesis 1 creation account the big bang evolution story includes all aspects of cosmic evolution from the big bang beginning, through the formation of stars and planets (especially the solar system) to the origin of life (which evolutionists say is from recycled star dust).3 Biological evolution (or the ‘progressive’ appearance of separate bursts of created life, according to Ross and his co-workers) involves only the last 3.8-billion-year sequence on planet Earth. This table shows 23 conflicts in the sequences of events alone.
It could hardly be said that the Bible is giving a simplified account of the big bang/evolution history of the universe. Yet those believers who hold to the notion that the ‘days’ of Genesis 1 have to be interpreted as long periods of time, deep time, also have a problem. Even though they might be strongly opposed to Darwinian evolution, yet, since they accept the same long-age assumptions as evolutionists regarding the ‘geological column’, the age of the cosmos and evolution of the planetary bodies, particularly earth, it follows that they believe in and promote the same order of appearance as evolutionists. Hence this table of event conflicts shows the same serious conflict between the Bible’s creation account and their cosmogony.4
Both describe a universe that began to exist (Genesis 1:1; Hebrews 11:3), as well as
Yes, I agree. This is the only real correspondence—a beginning in time. For this reason, in the 1950s and 60s, the atheist big bang believers were called ‘evangelicals’ by the atheist steady state believers. The steady state model has no origin in time, it is the eternal universe. And that has its own problems.5
the subsequent expansion of the universe (Isaiah 40:22, 42:5, 44:24, 45:12, 48:13, 51:13),
He clearly accepts the expansion of the universe as a fact. That ‘fact’ totally depends on the correct interpretation of cosmological evidence. My assessment of that evidence6,7 is that it is equivocal. The currently available observational evidence could fit either an expanding or a static universe. See Does observational evidence indicate the universe is expanding? (read both pts 1 & 2) for more on this.
But more importantly as a Christian one should be careful about blithely stating/believing/implying that that list of scriptures describe cosmological expansion.
I have been guilty of that mistake myself. But after looking into the Hebrew meaning of those passages I came to the conclusion that one could never exegete a meaning of cosmological expansion of the universe. Certainly not by a factor of 10. The most distant galaxies have redshifts z ~ 10 and we are supposed to be seeing them at an epoch only a few billion years after the big bang beginning. Nor by a factor of 1000, which would represent the supposed amount of expansion since big bang fireball, some 380,000 years after the first bang. Nor by nearly infinity (~1030) if you believe the cosmic inflation scenario to be true. Read Does the Bible really describe expansion of the universe?
all governed by constant laws of physics (Jeremiah 33:25), specifically by the pervasive law of decay (Romans 8:18–21).
God’s laws of physics can be trusted. In Jeremiah 33:25 the Lord Jehovah is telling us that His Word, His promises, can be trusted as much as the laws that govern the universe.8 But His Word says nothing about big bang fudge factors used to support a false model when tested against astronomical evidence.
Thus, the new evidence for an inflationary epoch (see Monday’s post) provides a powerful apologetic tool to argue for the authority of the Bible.
No, it doesn’t. If it turns out that the atheist community eventually reject the inflationary epoch for some other fairy dust, where will Jeff Zweerink and Hugh Ross be? They have developed their theology based on the theories of man.
Many secular cosmologists themselves doubt the idea that the inflationary epoch has been detected.9 That is the heart of the problem. The only source of truth for an apologetic is the plain reading of God’s Words, not some twisting and wresting the Scriptures to make them fit man’s atheistic theories. Scripture does not need man’s fanciful ideas to prove God’s authority in His Words. All Scripture needs is that you believe it.
He also cites Romans 8:18–21, as if these verses are referring to the ‘law of decay’.10 They are not; in them, the Lord gives us a picture of His future restoration of His once-perfect Creation from the bondage of the Curse. It is true that the Curse in part involves decay in the creation, which involves the law of decay in nature. But using them in this way, conflating this law and the Curse, gives the impression that prior to the Curse, the law would not have operated. Whereas the law of decay must have been in operation before God cursed Adam and the very creation itself. If that was not so, then Adam could not have digested his food (or even inflated his lungs) as these rely on that ‘law of decay’. 11
Unverified unknowns explain the unknown
According to astrophysicist Dr Richard Lieu,12
Cosmology is not even astrophysics: all the principal assumptions in this field are unverified (or unverifiable) in the laboratory …
This is the problem. Those, like Zweerink, who believe God used the big bang and all aspects of cosmic evolution, except for Darwinian biological evolution, to ‘create’, also misunderstand the true nature of cosmology. They mistakenly believe it is like repeatable testable experimental science, like I do in my research lab on earth. But it is not. It is quite different.
We have no access to the past and cosmology is rather unique because it is limited by what is called ‘cosmic variance’. We only see a limited picture of the universe. We can only attempt to understand that which is outside of what we can see through simulations (in computers with mathematical models). But we can’t really test those models, because we don’t know what a typical universe should look like. That is the limitation.
But we are told to just trust the cosmologists—trust man, after all it’s peer-reviewed! Yet cosmologists are limited by their own worldview. It is the basis on which they interpret all they can see. And all interpretations are based on unprovable assumptions.
Zweerink lists 4 different problems that Young Earth Creationists have with inflationary big bang models. His criticisms are of problems taken from an article written by biblical creationist Dr Danny Faulkner.13 Those problems are:
- Light travel time
- Gravitational lensing
- Quadrupole and octopole modes
- Scattering by electrons
I very briefly address each of these in turn below.
Light travel time
Why is the temperature of the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) so uniform when opposite sides of the universe have not had time (even in the presumed 13.8 billion years) to come into thermal equilibrium?14 This is a light travel time problem for big bang cosmology.
The fudge factor, cosmic inflation, was proposed to solve this problem, and several others as well. And he writes,
“…the BICEP2 Collaboration reported detection of the B-mode polarization of the CMB, which provides a smoking gun signature for inflation,…”.
But this is where cosmology starts to come unstuck.

Credit: BICEP2 Collaboration.
Has the smoking gun of the big bang been found? No. You would have to rule out all other possible explanations for the same evidence and that would be impossible. Cosmology is not even really science. It is an exercise in philosophy and that philosophy is really to support a godless atheistic worldview. 15 And even the atheistic big-bang-believing theorists are saying, ‘Hold on a minute!’ Some even spoke about a possible Nobel prize for the ‘smoking gun’ discovery but hey, not so fast with the Nobel prize! They have said it is too soon to claim a definitive proof—it could also be caused by other effects.
In fact, a significant controversy has already developed and is swirling around the blogosphere. As reported in Science,
“The biggest discovery in cosmology in a decade could turn out to be an experimental artifact—at least according to an Internet rumor. The team that reported the discovery is sticking by its work, however.” 16
Some experts have suggested that the polarized emission from dust in our galaxy can account for most of the swirls in the BICEP2 data and that the BICEP team made a mistake,17 making it more likely that the signal came from a source other than gravitational waves.
These rumours have been circulating for the past several weeks. On April 3rd 2014 I wrote,18 citing others in support as well, that they should not be so fast to claim a ‘proof’. Now that comment seems even more pertinent. This goes to what I said above about ‘hanging your theology’ on the theories of man. You may come unstuck faster than you might imagine.

Credit: NASA / ESA.
Gravitational lensing
As a result of the effect of a large concentration of mass, Einstein’s General Theory says that the mass of a closer cluster of galaxies will focus, hence magnify, light from a more distant galaxy that is behind the cluster. This is called gravitational lensing. From research by secular astrophysicists,19 it has been stated by creationists that this was not seen in the CMB radiation.
Zweerink wrote,
“Within recent months, scientists have published several reports detailing detections of the gravitational lensing in the CMB. These detections were made by the SPTpol Collaboration, the POLARBEAR Collaboration, and the Planck Collaboration.” [The 3 collaborations reference 3 papers in the original article.]
To look for such an effect in the CMB radiation requires a model to construct a template of what you would expect to get if the model was a true representation of the universe. The model used to generate the template is the standard dark-energy cold-dark-matter (LCDM) cosmology back to the time of the last scattering surface (LSS) of the big bang fireball at about 380,000 years after the big bang.
His reference20 states, “Gravitational lensing of the cosmic microwave background generates a curl pattern in the observed polarization.” This means the photons they see should have more of a swirl pattern one way than the other. The other papers make similar claims.21,22
They are looking to model the integrated effect on these swirl patterns from the matter in the universe over its evolution since that time 380,000 years after the big bang. Temperature fluctuations before that epoch are considered unlensed and must be separated from the model.
Two questions arise. Did they see this before they predicted it? Most importantly, is there any other possible mechanism that could result in the same patterns? On the first question, if so, then it’s not a prediction, but if not, the second question still applies.
Related to this are gravitational waves, which have not yet been detected on earth, where we have robust methods of testing any claim. In that sense they are an unknown as much as dark matter or dark energy. Yet in the alleged ‘smoking gun’ detection of inflation, evidence is also claimed for a signature of primordial gravitational waves, coming from before that LSS epoch.
In the CMB radiation only a putative secondary result, the product of the past influence of those waves on spacetime, can be mathematically extracted. It is totally model-dependent. Similarly with the evidence of gravitational lensing effects. But we don’t yet know if gravitational waves even exist. I am not saying they don’t, but we have not yet directly detected them.
And they may be right about gravitationally lensed galaxies (see Fig. 2) and this would have no bearing for or against creation by God. No creationist has suggested that. It was secular astrophysicists that expected lensing in the CMB and some said it was not observed.
However, Halton Arp promoted an alternative idea, that instead of some more distant galaxy’s image distorted by the foreground mass of the intervening cluster, these type of images show the products of ejections of new galaxies from the heart of active galactic nuclei.
Quadrupole and octopole modes
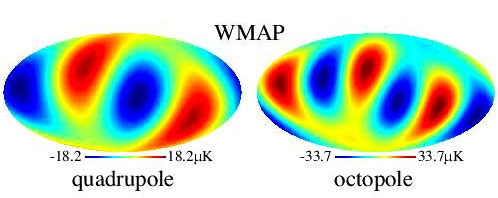
On this point Zweerink wrote:
“Even the most recent Planck data continue to show unexpected quadrupole and octupole modes in the CMB … Even though we lack a complete explanation for these ‘anomalies,’ they don’t require any new physics beyond standard inflationary big bang cosmology.” [emphasis added]
This refers to the way one can represent the small temperature fluctuations of the otherwise uniform 2.73 K temperature of the CMB radiation mapped across the sky. One can expand these fluctuations into spherical harmonic modes, starting at order 1, the dipole, then order 2, the quadrupole, then order 3, the octopole, etc.
What was discovered by secular cosmologists was that the natural axes related to these fluctuations, represented by these expansion terms, align with each other. This then gives a preferred direction for the universe, which has been dubbed the ‘Axis of Evil’.
I once pointed out23 that cosmologists, particularly Max Tegmark, had discovered this anomaly, and in his article Zweerink admits that the new Planck satellite data confirms this effect is real, not some measurement artifact of the Americans. He cites a few papers from the Planck collaboration team, and in one abstract the authors state:
“Although these analyses represent a step forward in building an understanding of the anomalies, a satisfactory explanation based on physically motivated models is still lacking.”24 [emphasis added]
This means that they still have no idea. Zweerink claims there is nothing remarkable in this. He says
“…they don’t require any new physics beyond standard inflationary big bang cosmology”.
But the paper he cites says:
“It may be due, in part, to chance alignments between the primary and secondary anisotropy, …. While this alignment appears to be remarkable, there was no model that predicted it, nor has there been a model that provides a compelling retrodiction.”25
The conclusion is that they put it down to chance alignment. And it seems like they need a new model to describe it—i.e. new physics is required. But definitely what Zweerink says is wrong—it misleads, if not deceives, those who take his word for it.
Scattering by electrons
Update (2 March 2018)
I first made this argument in 2006 based on the work of Prof. Lieu and others. If the big bang were true, the light from the fireball should cast a shadow in the foreground of all galaxy clusters. However new research (Xiao, W., Chen, C., Zhang, B., Wu, Y., and Dai, M., Sunyaev–Zel’dovich effect or not? Detecting the main foreground effect of most galaxy clusters, MNRASL 432, L41–L45, 2013) has thrown this conclusion into doubt. Prof. Lieu at the time wrote “Either it [the microwave background] isn’t coming from behind the clusters, which means the Big Bang is blown away, or … there is something else going on.” As it turns out that “something else” is contamination of the expected shadowing by radio emissions from the galaxy clusters themselves.
Without anything to contradict this new result, and the analysis seems strong, one must entertain the possibility that the anomaly first found by Lieu et al in 2006 has been adequately explained. The problem of course is that astrophysics is not exactly operational science. At best this no-shadow argument is now equivocal and hence I suggest that it should no longer be used as an argument against the big bang hypothesis.
When one measures the CMB radiation in the direction of a cluster of galaxies, the inverse-Compton effect alters the intensity of the radiation, by a scattering process. Photons are scattered to higher frequencies, a thermal effect, but in all directions and as a result there are fewer low energy photons and more higher energy photons than one would expect in the CMB radiation up to a frequency of about 218 GHz.26 Astronomers call this distortion of the cosmic background the Sunyaev-Zel’dovich Effect (SZE). If the source is behind the cluster the SZE should produce a net cooling effect, a decrement in temperature (or a shadow) in the foreground of the cluster in the line of sight of the observer. See Fig. 4.

Credit: astro.uchicago.edu/sza/primer.html
Richard Lieu analysed 31 galaxy clusters and found that on average they did not cast a shadow in their foreground from the supposed background light source of the big bang fireball.27 He found a lack of evidence of shadows in the CMB photons from ‘nearby’ clusters of galaxies using the highly accurate WMAP satellite measurements of the CMB. But if the CMB radiation is truly from the big bang it is the ultimate background source and galaxy clusters should cast shadows.
At that time Lieu said, “Either it [the microwave background] isn’t coming from behind the clusters, which means the Big Bang is blown away, or … there is something else going on…”28
In his article Zweerink wrote:
“Research published last year demonstrated a measurement of both the thermal and kinetic Sunyaev-Zel’dovich effect from a massive galaxy cluster. In other words, the expected distortion in the CMB has been detected.” [emphasis added]
It seems that Zweerink is using a sort of bluff and bluster technique. The paper he cites measured the thermal and kinetic SZ signals in a single cluster and its sub-clusters. So what? No argument there. The kinetic effect was used to detect motions of subclusters. That is not the point here.
Lieu measured the thermal SZE in 31 clusters. Lieu found that only one quarter of the sample of 31 showed a net decrement due to the thermal SZE. If the CMB radiation was from the big bang all clusters should show a decrement or a shadowing effect. They don’t.
Conclusion
Cosmology really is not science in the sense of repeatable laboratory experiments. One must make many unprovable assumptions to proceed with the analysis of the observational data. And as someone once said, there are as many cosmologies as there are cosmologists. Whom do you believe?
As science advances and man’s knowledge increases either we must accept what God has said as truth in His Word or we will forever be searching for an answer that relies on so many unknowns. These unknowns then become the replacement for the Creator in the search for an answer to fundamental questions about the universe.
But one conclusion I can definitely draw from this analysis is that Dr Zweerink has not examined the evidence with a critical mind and contrasted it with the Word of God. Just on the Genesis 1 sequence of events alone one can conclude that the big bang cosmology is not what the Author of Genesis had in mind.
References
- J. Zweerink, A Response to Four Young-Earth Objections to Inflation, www.reasons.org/articles/a-response-to-four-young-earth-objections-to-inflation, 24 April, 2014. Return to text.
- See also Hartnett, J.G., 6-day creation of the universe, biblescienceforum.com, January 3, 2014. Return to text.
- This is the notion that it all first started with hydrogen that was eventually fused in the centres of exploding stars to all the elements needed for life. Some even suggest life itself, or precursor molecules of life, were carried to earth on a comet or an asteroid. Return to text.
- Not surprisingly, ‘progressive creationists’ have developed some strategies to try to downplay the conflict; e.g. that the Bible can be read as saying that the sun/moon/stars only ‘appeared’ (e.g. from the dissipation of some cloud cover) on the 4th Day, having already existed for millions of years; this despite the fact that the Hebrew word God used is ‘made’, and the Hebrew for ‘appeared’ is not used. This highlights the problem with such attempts to ‘harmonize’ the Bible with secular science, that the obvious meaning of the text is sacrificed. It is made to look as if the Bible has been misleading believers for centuries prior to the discovery of this modern neo-gnostic ‘key’ to understanding what it really says—e.g. millions of years, not six days with an evening and a morning. Return to text.
- Before my own repentance and knowledge of the saving grace of our Lord Jesus Christ, I was also an atheist and a cosmologist. I favoured the steady state model back in the mid to late 1960s because there was no beginning in time. Therefore I believed that no beginning meant no Creator and I could do whatever I liked. But the hypothesis of no beginning is seriously impacted by entropy. Sufficient to say here that useful energy is constantly lost as entropy inexorably increases in the universe. Return to text.
- Does observational evidence indicate the universe is expanding? part 1: the case for time dilation Return to text.
- Does observational evidence indicate the universe is expanding? part 2: the case against expansion Return to text.
- Though of course God can add to them when He chooses; see creation.com/miracles-and-science. Return to text.
- See Hey, not so fast with the Nobel Prize!. Return to text.
- Aka the Second Law of Thermodynamics. Return to text.
- But Rossists have a problem with the whole notion of a cursed creation in any case. Due to their acceptance of the geological age system for fossils, they have to accept cancer, infection, bloodshed and violence in the world long before Adam; so how did the Curse affect the ‘whole creation’ anyway? In addition, since fossil thorns are found deep in the record, God’s pronouncement of thorns as a consequence of the Adamic Curse no longer seems trustworthy. Return to text.
- Richard Lieu, LCDM cosmology: how much suppression of credible evidence, and does the model really lead its competitors, using all evidence? 17 May 2007, arxiv.org/pdf/0705.2462v1.pdf Return to text.
- D. Faulkner, Comments on the Cosmic Microwave Background, www.answersingenesis.org/articles/arj/v7/n1/cosmic-microwave-background, March 2014. Return to text.
- Light-travel time: a problem for the big bang Return to text.
- https://creation.com/cosmology-is-not-even-astrophysics. Return to text.
- Blockbuster Big Bang Result May Fizzle, Rumor Suggests, 12 May 2014, news.sciencemag.org/physics/2014/05/blockbuster-big-bang-result-may-fizzle-rumor-suggests Return to text.
- Rumours swirl over credibility of big bang ripple find, 13 May 2014, www.newscientist.com/article/dn25558-rumours-swirl-over-credibility-of-big-bang-ripple-find.html#.U3VC7vmSxFv Return to text.
- Ref. 9. Return to text.
- No sign of gravitational lensing in the cosmic microwave background. Return to text.
- D. Hanson et al. (SPTpol Collaboration), Detection of B-Mode Polarization in the Cosmic Microwave Background with Data from the South Pole Telescope, Phys. Rev. Lett. 111: 141301, 30 September, 2013. Return to text.
- P. A. R. Ade et al. (POLARBEAR Collaboration), Evidence for Gravitational Lensing of the Cosmic Microwave Background Polarization from Cross-Correlation with the Cosmic Infrared Background, Phys. Rev. Lett. 112: 131302, 2014. Return to text.
- P. A. R. Ade et al. (Planck Collaboration), Planck 2013 results. XVII. Gravitational lensing by large-scale structure, Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2013; arxiv.org/pdf/1303.5077v1.pdf. Return to text.
- CMB Conundrums. Return to text.
- P. A. R. Ade et al. (Planck Collaboration), Planck 2013 results. XXIII. Isotropy and statistics of the CMB, Astronomy &Astrophysics, 2013, arxiv.org/pdf/1303.5083v3.pdf. Return to text.
- C. L. Bennett et al., SEVEN-YEAR WILKINSON MICROWAVE ANISOTROPY PROBE (WMAP∗) OBSERVATIONS: ARE THERE COSMIC MICROWAVE BACKGROUND ANOMALIES? Astrophysical Journal Supp. 192: 17, 2011, iopscience.iop.org/0067-0049/192/2/17/pdf/0067-0049_192_2_17.pdf. Return to text.
- There is also a second order kinematic or kinetic effect due to bulk motion of the electrons in the intercluster medium. Return to text.
- R. Lieu, J.P.D. Mittaz and Shuang-Nan Zhang, “The Sunyaev-Zel’dovich effect in a sample of 31 clusters: A comparison between the X-ray predicted and WMAP observed decrement," Astrophysical Journal 648(1): 176, 2006. Return to text.
- Big Bang’s Afterglow Fails Intergalactic ‘Shadow’ Test, www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2006/09/060905104549.htm. Return to text.






Readers’ comments
Comments are automatically closed 14 days after publication.